Value creation in the corporate context means taking various resources such as time, money, materials, and knowledge and combining them to produce goods or services. The important thing is that these goods or services are worth more to customers than the cost of the resources used to produce them. If a company does this successfully, it means that it makes a profit and increases in value over time. But how does communication help to increase this value?
The Communication Value Circle #
To answer this question, a framework was developed, called the Communication Value Circle (CVC). It depicts the most important ways that corporate communication can add value and summarizes them in an easy-to-understand model. The framework was developed by German communication researchers Ansgar Zerfass and Christine Viertmann and is based on extensive literature research and interviews with CCOs (Chief Commercial Officer) of global corporations.
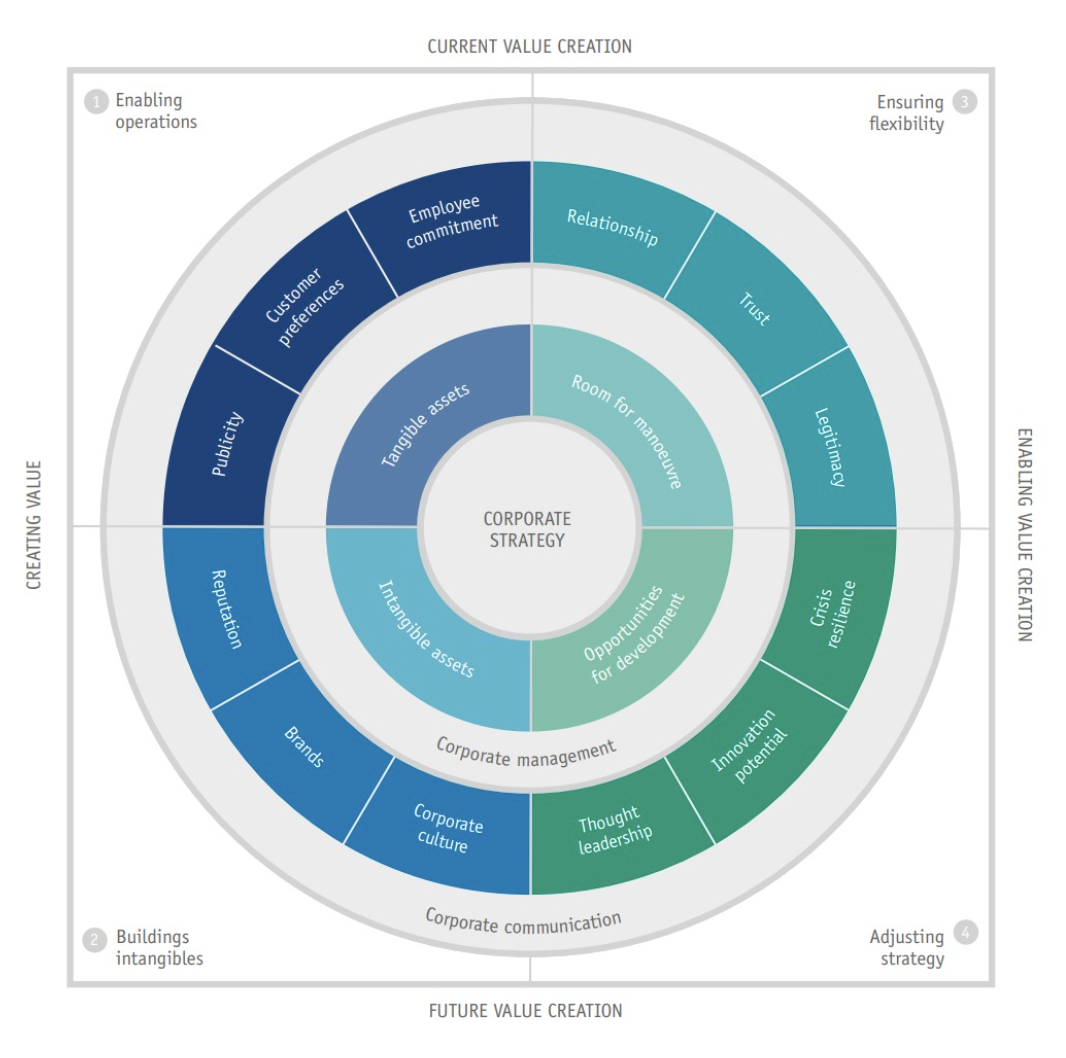
The Structure
The CVC comprises two strategic layers: the corporate strategy level (inner circle) and the communication strategy level (outer circle). The corporate strategy level in the CVC includes four main company objectives:
- tangible assets (things you can touch like machinery or buildings)
- intangible assets (non-physical things like brand reputation or customer loyalty)
- room for maneuver (ability to navigate through changing market conditions)
- opportunities for development (chances to improve)
The tangible and intangible assets contribute to a company's worth, while the room for maneuver and opportunities for development help the company to grow. Consider these goals as the pillars that structure corporate value - they underline everything from sales and human resources management to corporate communications.
This leads us to the outer circle of the CVC - the area of communication strategy. For each of the four overall business objectives, this outer circle illustrates how communication contributes to achieving these corporate objectives within the four areas: enabling operations, building intangibles, ensuring flexibility, and adapting strategy.
Twelve Communication Value Dimensions
Each of the four communication value contributions is subdivided into three dimensions that can be measured using established key performance indicators (KPIs).
Enabling Operations
... is about building visibility and fostering relationships with key stakeholders like customers and employees. It particularly contributes to tangible assets by enhancing awareness of the company's offerings and stimulating business processes, directly linking to the creation of material value.
- Publicity: Gaining visibility and awareness in the market.
- Customer Preferences: Influencing consumer attitudes towards products or services.
- Employee Commitment: Ensuring that employees align with the goals, values, and norms of the company.
Building Intangibles
... involves communication strategies to build non-physical assets like reputation and brand. It adds value by enhancing the company's identity and public image, hence increasing its overall worth.
- Reputation: Creating a positive and trustworthy perception among stakeholders.
- Brands: Building a unique mental image of the organization and its products/ services within stakeholders' minds.
- Corporate Culture: Fostering a shared understanding of values, beliefs, and expectations within the organization.
Ensuring flexibility
... supports a company's ability to adapt and move confidently in a changing environment. It builds trust-based relationships and validates the company's actions, thus providing it with leeway or room for maneuver. This enhances the stability and adaptability of the company, adding value to its operations.
- Relationships: Developing and maintaining high-quality connections with key stakeholders.
- Trust: Enhancing confidence among stakeholders in the organization's consistencies and dependability.
- Legitimacy: Ensuring organizational actions align with socially accepted norms, values, and expectations.
Adapting Strategy
... enhances a company's strategic positioning by fostering new ideas, spotting trends, and building resilience against crises. Listening and adjusting to changes in markets and society helps identify new development opportunities, thereby adding substantial value to the company.
- Thought Leadership: Positioning the organization as a leading source of innovative ideas.
- Innovation Potential: Recognizing opportunities for new products and strategies and understanding market trends.
- Crisis Resilience: Identifying potential threats and proactively preparing for various crisis situations.
The Concept of Alignment
One of the most valuable aspects of the CVC is its main underpinning principle: alignment. It emphasizes the need for all communication activities to align seamlessly with the overall corporate strategy. In order to convert corporate strategy into an effective communication strategy, the following steps come into play:
- Analyse: Reflect on the organization’s current strategic direction and potential areas where communication could add value.
- Derive: From the corporate objectives (outlined in the inner circle of CVC), identify core communication targets (described in the outer circle of CVC).
- Define: Break down these communication targets into measurable action steps, using defined key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Verify: Continually evaluate to ensure all communication activities align with the defined targets and overall corporate goals.
By providing this clear, navigable roadmap, the CVC offers organizations a reliable framework for developing efficient and strategic communication approaches that inherently align with overall business goals. The CVC is not merely a communication tool; it's a strategic instrument that contributes directly to the company's overall business success.
Where to go from here #
For a deeper understanding of the CVC, take a look at the publication referenced below. This resource provides details on the KPIs that help determine the success of each dimension. It also provides a detailed explanation of the tools and methods that can be used to measure these KPIs.
References #
Volk, S. C., Berger, K., Zerfass, A., Bisswanger, L., Fetzer, M., Köhler, K. (2017). How to play the game.
Strategic tools for managing corporate communications and creating value for your organization (Communication Insights, Issue 3). Leipzig, Germany: Academic Society for Management & Communication. Available online at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324592972_How_to_play_the_game_Strategic_tools_for_managing_corporate_communications_Communication_Insights_Issue_3
This article is a student-written report on a part of the course Strategic organisational communication in the 3rd semester of the M.A. program in content strategy. It has been authorized by the instructor Lisa Dühring.

